Aging gracefully is a gift, but it often brings new health considerations, with diabetes being a significant concern for many over 45. The good news? With a proactive approach to nutrition and lifestyle, you can absolutely thrive, manage diabetes after 45 and maintain a vibrant quality of life. At Mature Nutrition, we believe in empowering you with the knowledge to make informed choices.
Understanding Diabetes: A Mature Perspective
Diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes, is more prevalent as we age. It’s characterized by the body not effectively using insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar. While it may seem daunting, understanding its impact is the first step towards masterful management.
Left unmanaged, high blood sugar can lead to serious complications for mature adults, including:
- Heart and Blood Vessel Disease: Increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and narrowed blood vessels.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Often starting in the hands and feet, causing tingling, numbness, pain, or loss of feeling.
- Kidney Disease (Nephropathy): Can progress to kidney failure, potentially requiring dialysis or a transplant.
- Eye Damage (Retinopathy): Risk of cataracts, glaucoma, and damage to the retina, which can lead to vision loss or even blindness.
- Cognitive Decline: A higher risk of memory and thinking problems, including an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Increased Risk of Falls: Due to vision issues, nerve damage, and potential medication side effects.
- Depression: The emotional toll of managing a chronic condition can be significant.
- Slow-Healing Wounds: Minor cuts and blisters can become serious infections.
Early detection and consistent management are paramount to mitigating these risks and ensuring your long-term well-being.
Nourishing Your Body: The Power of Food
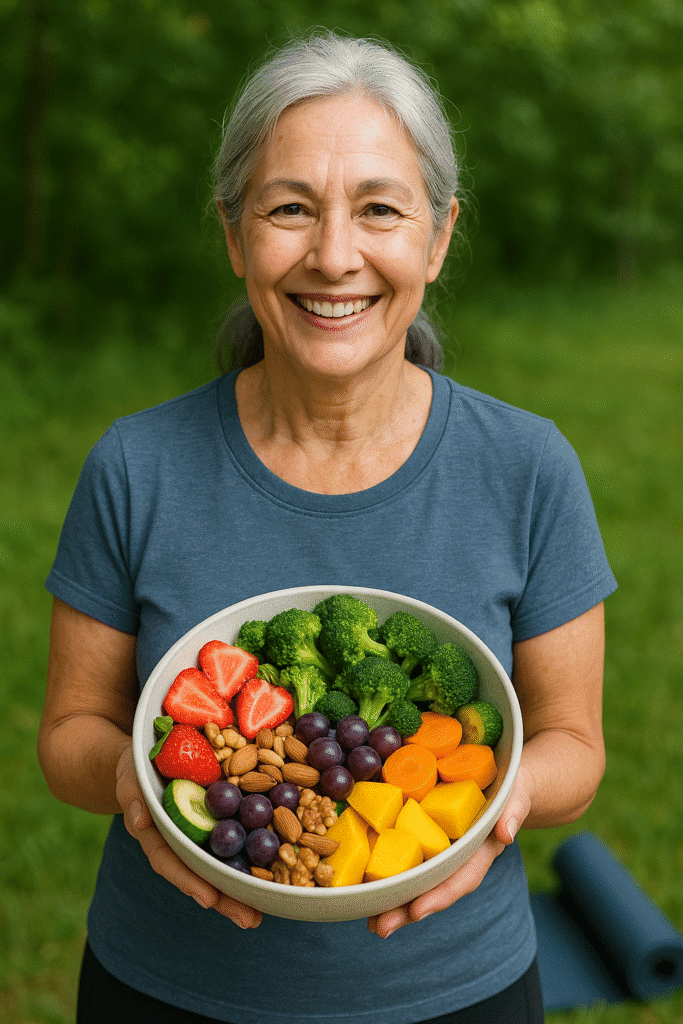
What you eat plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. Focusing on nutrient-dense, whole foods with a lower Glycemic Index (GI) can make a profound difference. The Glycemic Index measures how quickly a food raises your blood sugar.
Foods to Embrace:
- Low GI Fruits and Vegetables: Many vibrant options are your allies! Consider:
- Berries: Raspberries, Strawberries, Blueberries. These are packed with antioxidants.
- Citrus Fruits: Grapefruit, Oranges.
- Leafy Greens: Dandelion greens, Lettuce, Rapini.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, Cauliflower, Cabbage.
- Root Vegetables: Carrots, Radishes, Jicama.
- Other Gems: Cucumber, Green beans, Asparagus, Artichoke.
- Lean Proteins: Essential for satiety and muscle maintenance.
- Seafood: Alaska Pollock, Anchovy, Bass, Bluefish, Cod, Flounder, Haddock, Halibut, Salmon, Shrimp, Tilapia, Tuna, Trout, Mackerel, Mussels, Oysters. Most seafood has a GI of 0 and is calorie-efficient.
- Poultry: Chicken breast, Chicken meat, Turkey.
- Other Lean Meats: Bison meat, Goat meat.
- Healthy Fats: Support overall health and can help with blood sugar regulation. Examples include avocados, nuts (almonds, hazelnuts, pecans), seeds (pumpkin, sesame, flaxseed), and olive oil. The Mediterranean eating pattern, emphasizing these fats, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, is often recommended for improving glucose metabolism and reducing cardiovascular risk.
- Legumes: Kidney beans, Lentils, Lima beans, Mung beans, Adzuki beans. These offer excellent fiber and protein.
- Whole Grains: While some grains can be high on the GI scale, others are better choices. Focus on those with a lower GI when possible.
Foods to Limit or Avoid:
- High GI Fruits: Dates, Watermelon, Raisins, Dried Figs.
- Sugary Beverages: Cranberry juice, Grape juice, Ginger ale. These can cause rapid blood sugar spikes.
- Refined Grains and Sugars: Flour, Cornmeal, Glutinous rice , White bread. These contribute to higher blood sugar levels.
- Processed Foods: Often contain hidden sugars and unhealthy fats.
- Sweeteners: High-fructose corn syrup, white sugar, brown sugar.
Supplements and Natural Support
While supplements should never replace medical advice or prescribed medications, certain natural compounds have shown promise in supporting blood sugar management. Always consult your healthcare provider before adding any supplements to your routine, especially if you are on medication.
Research suggests potential benefits from:
- Cinnamon: May help the body respond better to insulin.
- Magnesium: Many people with Type 2 diabetes are deficient. Supplementation may promote healthy insulin production and action.
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA): An antioxidant that may improve insulin sensitivity and is used for diabetic neuropathy.
- Vitamin D: Deficiency is linked to an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes. Adequate levels may improve insulin function.
- Berberine: A compound from certain plants that may help reduce fasting blood sugar.
- Ginseng: May help decrease post-meal blood sugar.
- Fenugreek: Contains fiber that may slow carbohydrate digestion and absorption.
Remember, a balanced, whole-food diet is the foundation of managing diabetes. Supplements can be a supportive addition, but they work best in conjunction with a healthy eating plan and regular physical activity.
Beyond the Plate: Lifestyle for Longevity
Nutrition is powerful, but a holistic approach to diabetes management includes lifestyle factors:
- Regular Physical Activity: Even moderate exercise, like a daily walk, can significantly improve glucose levels and insulin sensitivity.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight or losing excess weight is a primary factor in preventing and managing Type 2 diabetes.
- Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can impact blood sugar. Incorporate relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or hobbies you enjoy.
- Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep can negatively affect insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Regular Check-ups: Consistent monitoring of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol, along with annual eye and kidney screenings, is vital.
Your Path to a Healthier Future
Living with diabetes doesn’t mean sacrificing enjoyment or vitality. By understanding the foods that nourish your body, exploring supportive supplements with professional guidance, and embracing a healthy lifestyle, you can take charge of your health. At Mature Nutrition, we’re here to support you on this incredible journey. Here’s to sweet harmony and a healthier, happier you!
Check Out These Recipes To Help Manage Glucose Levels
Sources:
- Diabetes and Older Adults – Endocrine Society
- Type 2 diabetes – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic
- Life with diabetes: What happens as we age? – Mayo Clinic Health System
- Tip Sheet: Managing Complications of Diabetes in Later Life – Health in Aging

Leave a Reply